CBD vs. THC: How Do They Differ?
CBD vs. THC: How Do They Differ?
Introduction
The journey of understanding the cannabis plant's compounds, particularly cannabidiol (CBD) and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), began in the early 1940s. While both have been known for decades, ongoing research continues to unravel their distinctive characteristics and medical potentials. In recent years, heightened awareness and education have propelled CBD and THC into the mainstream.
In this blog post, we delve into the similarities and differences between these two compounds, exploring their effects on the body, potential benefits, and how they navigate the complexities of the U.S. legal system.
CBD: A Brief Overview
Cannabidiol, or CBD, stands as one of the primary cannabinoids found in cannabis sativa plants. These plants can be categorized based on their CBD and THC production levels, with Type I and Type II considered marijuana and Type III classified as hemp. Notably, CBD can be derived from any cannabis sativa plant, but legal status in the U.S. hinges on it coming specifically from hemp.
Related: Cannabis Strains 101-Everything You Need To Know.
THC: The Psychoactive Element
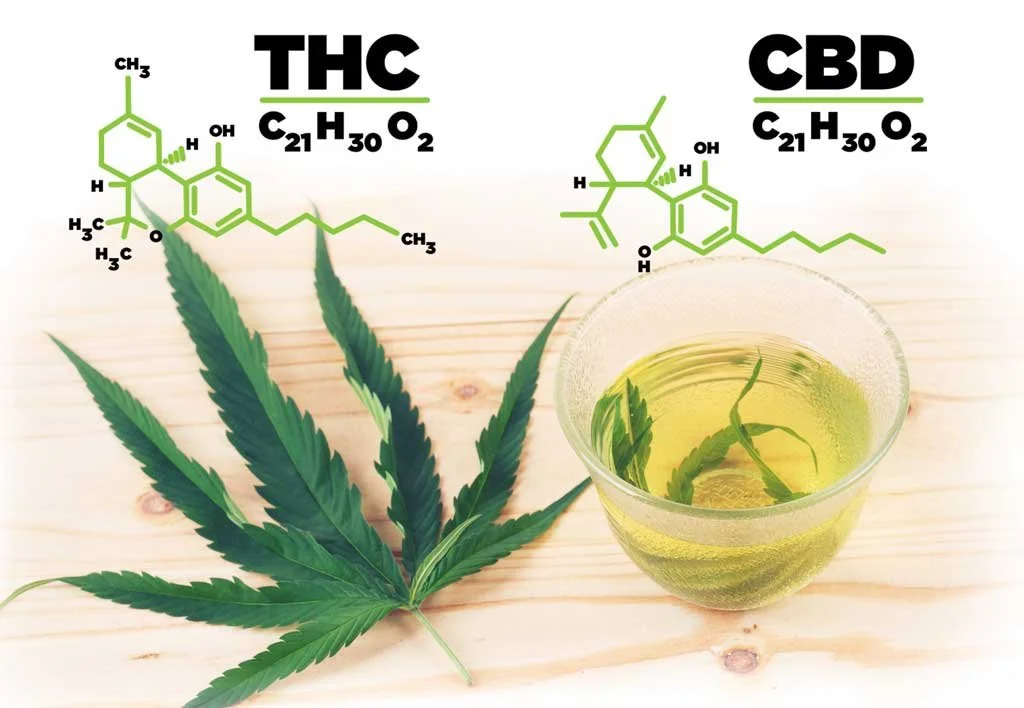
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is another major cannabinoid in cannabis sativa plants, notorious for inducing the intoxicating "high" associated with cannabis use. Understanding the distinctions between CBD and THC requires delving into their chemical structures and how they interact with the body's endocannabinoid system.
Chemical Structure and Interaction with Receptors
From a chemical standpoint, THC and CBD share the same formula but possess different structures. CBD consists of two 6-membered rings, while THC includes an additional 6-membered ring formed via the attachment of a carbon and an oxygen atom. These differences influence how they bind with the endocannabinoid system receptors – CB1, largely in the brain, and CB2, mostly in the immune system.
THC's psychoactive effects primarily result from its binding with CB1 receptors. On the contrary, CBD exhibits little affinity for either CB1 or CB2 receptors. Despite common misconceptions, CBD is psychoactive, affecting the mind without inducing intoxication or impairing functionality.
Legality and Drug Testing
In the U.S., hemp-derived CBD products are legal under the 2018 Farm Bill as long as they contain no more than 0.3% THC. However, discrepancies arise due to varying state laws, leading to mislabeling and confusion. Drug tests typically focus on detecting THC rather than CBD. It's crucial to consider the THC content in CBD products, as even hemp-derived ones may result in a positive THC test. Consulting a medical professional and understanding specific drug tests is advisable for those concerned about potential THC exposure.
Potential Side Effects
THC use is associated with side effects like dry mouth, intoxication, disorientation, paranoia, and, in extreme cases, panic attacks and psychosis. CBD, on the other hand, has been deemed non-abusive, with high doses leading to sleepiness and potential long-term effects on the liver. Adverse effects from CBD are often linked to other ingredients in the product rather than CBD itself.
Similarities and Potential Benefits
CBD and THC, despite their differences, share some similarities in their effects, particularly in managing sleep issues and physical pain. CBD, known for alleviating stress and anxiety, can complement THC's benefits when consumed together. For instance, a 1:1 THC and CBD mix called Nabiximols has been approved in 27 countries for relieving symptoms of multiple sclerosis and cancer-related pain.
Read Also: Unveiling the Green Wonder: Facts About Cannabis.
Ingestion Methods
Both CBD and THC can be consumed in various ways, including smoke inhalation, vapor inhalation, edibles, and oils or extracts. Understanding the ingestion methods allows users to tailor their cannabis experience to their preferences.
The Bottom Line
As our understanding of CBD and THC evolves, their unique properties and potential benefits continue to emerge. From their distinct chemical structures to their interactions within the body, these compounds offer a fascinating landscape for researchers and users alike. Navigating the legal complexities and potential health impacts requires a nuanced understanding, emphasizing the importance of informed choices and responsible use in the rapidly expanding world of cannabis-derived products.
FAQ
-
No, the legality of CBD and THC varies. Hemp-derived CBD products, with less than 0.3% THC, are legal under the 2018 Farm Bill at the federal level. However, state laws differ, with some allowing adult recreational and medical cannabis use, while others restrict it.
-
CBD is psychoactive, meaning it affects the mind, but it does not induce intoxication or impair function. Unlike THC, which binds to CB1 receptors, CBD has little affinity for these receptors. When consumed together, CBD can mitigate some of the intoxicating effects of THC.
-
CBD and THC interact differently with the endocannabinoid system due to their distinct chemical structures. THC binds with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, primarily in the brain and immune system. In contrast, CBD has little affinity for these receptors, influencing the body's response to external stressors without inducing a psychoactive high.
-
Yes, it is possible. Drug tests typically focus on detecting THC, and even hemp-derived CBD products may contain trace amounts of THC (up to 0.3%). To avoid this risk, individuals concerned about THC exposure should consider using broad spectrum CBD or CBD isolate, which exclude THC entirely.
-
CBD and THC, when consumed together, can compound their benefits. Both have been shown to help manage sleep troubles and physical pain. Clinical studies suggest that combinations like Nabiximols (1:1 THC and CBD) can be effective in relieving symptoms of multiple sclerosis and cancer-related pain, showcasing the potential synergy between these compounds